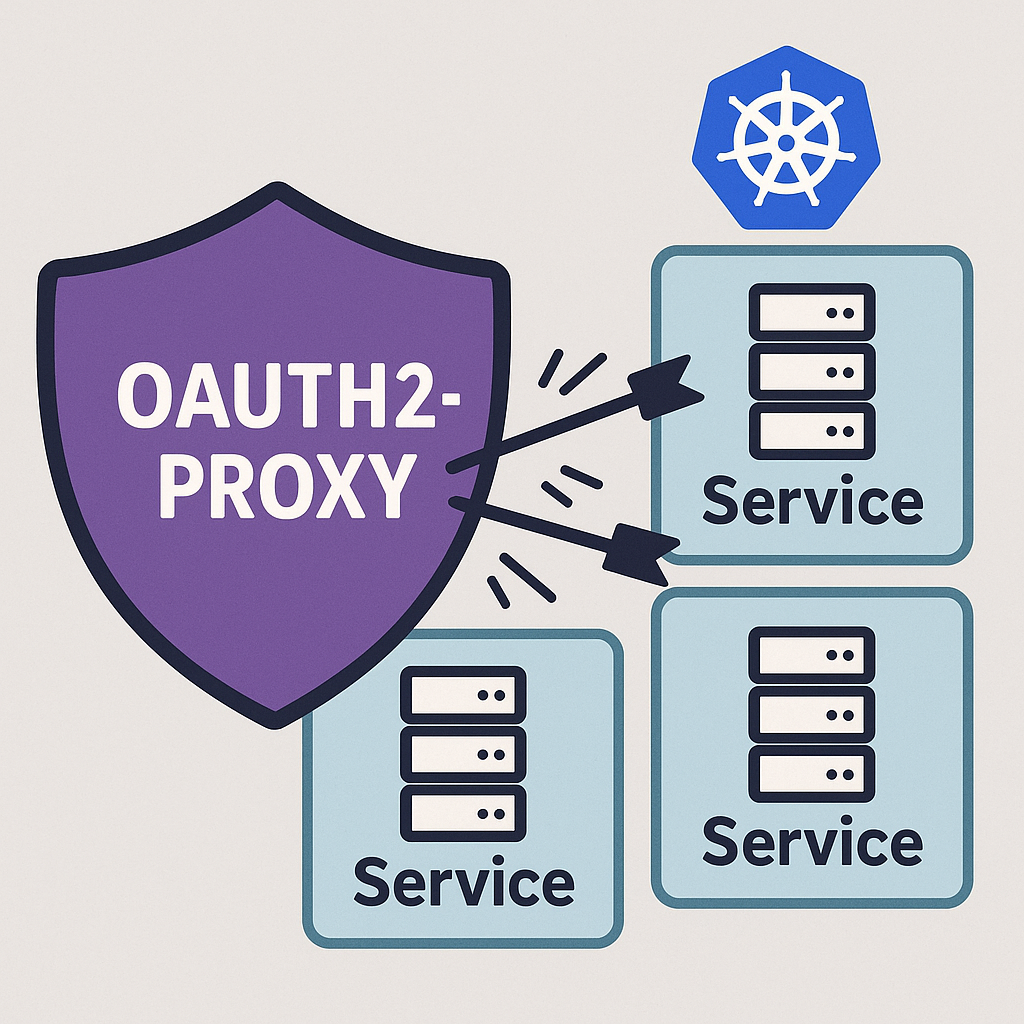
The original post wrote about oauth2-proxy over seven years ago was quite popular at the time and attracted a lot of organic traffic to my blog, which still benefits my SEO today. Since the tutorial had become outdated, I decided to rewrite it.
What we have
We have a Kubernetes cluster with several web services deployed for internal use.
What we want to achieve
We want to expose our internal web services to the Internet, but restrict access by requiring authorization. Access should be granted only to users authenticated through our Identity Provider (such as Google, GitHub, Keycloak, etc.).
Assumptions
For simplicity, let’s assume that both ingress-nginx and cert-manager are already deployed in the cluster.
I will use Pocket ID as Identity Provider in this tutorial. Configuration slightly differs for different providers. Check the official documentation for your provider.
For the examples in this guide, I’ll use my alikhil.dev domain:
– pocket-id.k8s.alikhil.dev - will be used for Pocket ID
-
k8s.alikhil.dev- will be used for oauth2-proxy. I recommend to have higher domain for oauth2-proxy service for easier cookie setup. -
*.k8s.alikhil.dev- reserved for services deployed for internal usage
Preparation
DNS
I have added two DNS records:
Arecord for k8s.alikhil.dev pointing to ingress-nginxLoadBalancerIP address in the cluster (kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx | grep LoadBalancer)CNAMErecord for*.k8s.alikhil.devpointing tok8s.alikhil.dev
Install Pocket ID
helm repo add anza-labs https://anza-labs.github.io/charts
helm upgrade --install pocket-id anza-labs/pocket-id -f ./values/pocket-id.yaml
Values for pocket-id
persistence:
data:
enabled: true
ingress:
# -- Specifies whether ingress should be enabled.
enabled: true
# -- Ingress class name.
className: "nginx"
# -- Annotations to add to the ingress.
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
kubernetes.io/ingress.allow-http: "true"
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
# -- Ingress host configuration.
host: pocket-id.k8s.alikhil.dev
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# -- List of TLS configurations for the ingress.
tls:
- secretName: pocket-id-tls
hosts:
- pocket-id.k8s.alikhil.dev
Configure PocketID
Go to https://pocket-id.k8s.alikhil.dev/signup/setup and set initial configuration for Pocket ID.
Then add your passkey.
Create developers group and add yourself to the list of members.
After that, go to OIDC clients page and create one for oauth2-proxy. Set proper callback url.
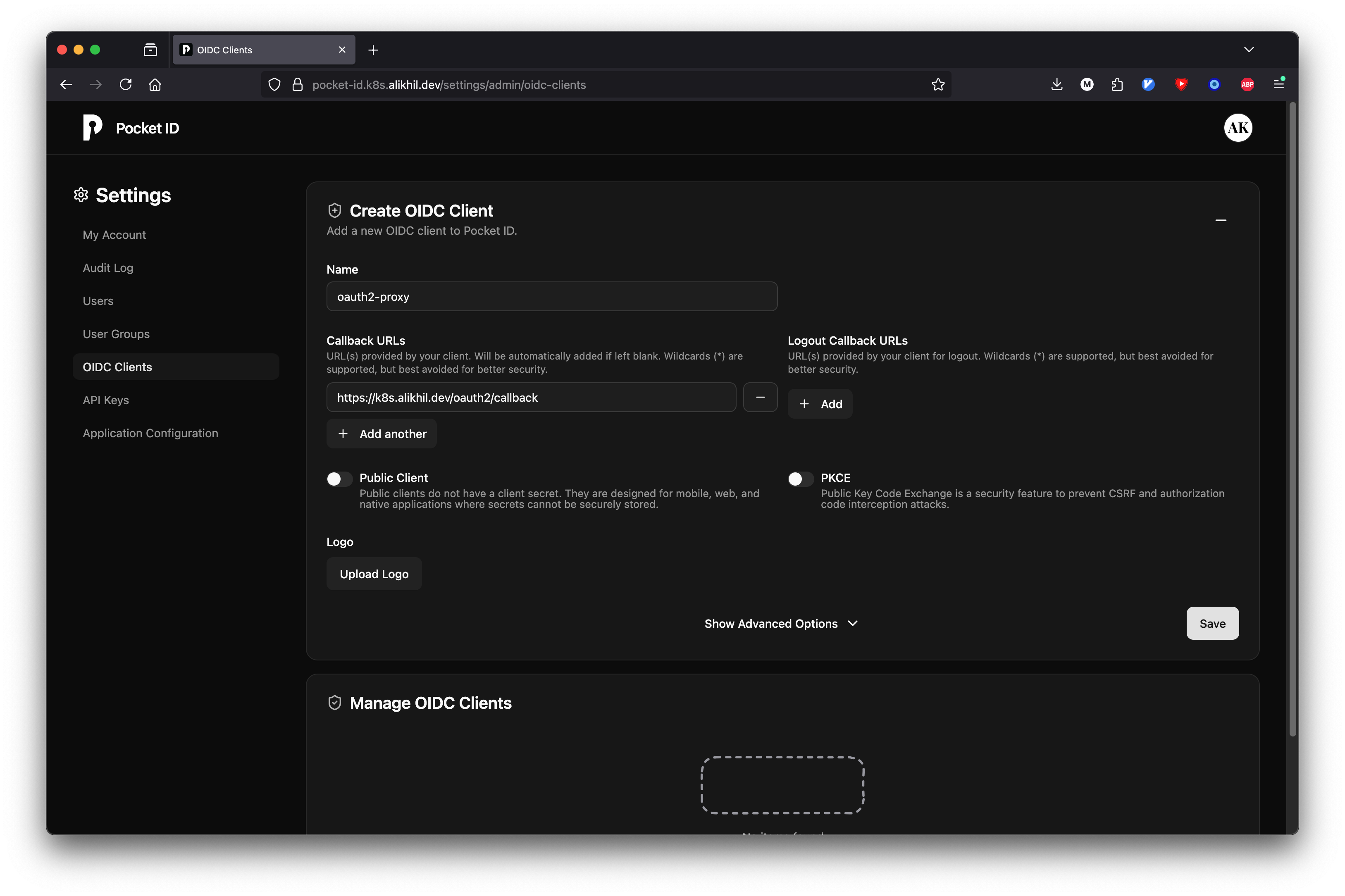
Save generated Client ID and Client Secret for later use.
Installing oauth2-proxy
I am using raw k8s secrets in this tutorial, but I highly recommend storing secrets in Vault or similar services and use External Secretes Operator to deliver them to kubernetes.
kubectl create secret generic oauth2-proxy-secrets --from-literal=client-id=$CLIENT_ID --from-literal=client-secret=$CLIENT_SECRET --from-literal=cookie-secret=$(openssl rand -base64 32 | head -c 32 | base64)
helm repo add oauth2-proxy https://oauth2-proxy.github.io/manifests
helm install oauth2-proxy oauth2-proxy/oauth2-proxy -f values/oauth2-proxy.yaml
Adjust domains in values for oauth2-proxy
# Oauth client configuration specifics
config:
existingSecret: oauth2-proxy-secrets
cookieName: "general-oauth2"
# Default configuration, to be overridden
configFile: |-
email_domains = [ "*" ]
upstreams = [ "file:///dev/null" ]
skip_provider_button = true
allowed_groups = [ "developers", "admins" ]
cookie_secure = false
cookie_domains = [".k8s.alikhil.dev", "k8s.alikhil.dev"]
whitelist_domains = [ "*.k8s.alikhil.dev", "k8s.alikhil.dev" ]
cookie_samesite = "lax"
cookie_csrf_per_request = true
cookie_csrf_expire = "15m"
pass_access_token = true
pass_authorization_header = true
provider = "oidc"
provider_display_name = "PocketID"
reverse_proxy = true
scope = "openid profile email groups"
session_store_type = "redis"
set_xauthrequest = true
set_authorization_header = true
silence_ping_logging = true
skip_auth_preflight = true
ssl_insecure_skip_verify = true
ssl_upstream_insecure_skip_verify = true
insecure_oidc_allow_unverified_email = true
oidc_issuer_url = "https://pocket-id.k8s.alikhil.dev"
redirect_url = "https://k8s.alikhil.dev/oauth2/callback"
# to reduce log amount
request_logging = false
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
path: /
# Only used if API capabilities (networking.k8s.io/v1) allow it
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# Used to create an Ingress record.
hosts:
- k8s.alikhil.dev
labels: {}
annotations:
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-origin: '*'
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors: 'true'
kubernetes.io/ingress.allow-http: "false"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
tls:
# Secrets must be manually created in the namespace.
- secretName: oauth2-proxy-tls
hosts:
- k8s.alikhil.dev
# Configure the session storage type, between cookie and redis
sessionStorage:
# Can be one of the supported session storage cookie|redis
type: redis
redis:
existingSecret: ""
password: ""
passwordKey: "redis-password"
clientType: "standalone"
# Enables and configure the automatic deployment of the redis subchart
redis:
# provision an instance of the redis sub-chart
enabled: true
architecture: standalone
auth:
enabled: false
master:
persistence:
enabled: false
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
Testing
Install whoami
To check oauth2-proxy we need a dummy service. I will use whoami helm chart for this.
helm repo add cowboysysop https://cowboysysop.github.io/charts/
helm install whoami cowboysysop/whoami
Values for whoami helm chart
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
kubernetes.io/ingress.allow-http: "true"
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
# put oauth2-proxy domain here
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: "https://k8s.alikhil.dev/oauth2/start?rd=https://$host$request_uri$is_args$args"
# service-name.namespace-name
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: http://oauth2-proxy.oauth-example.svc.cluster.local:80/oauth2/auth
hosts:
- host: whoami.k8s.alikhil.dev
paths:
- /
tls:
- hosts:
- whoami.k8s.alikhil.dev
secretName: whoami-cert
Perform test
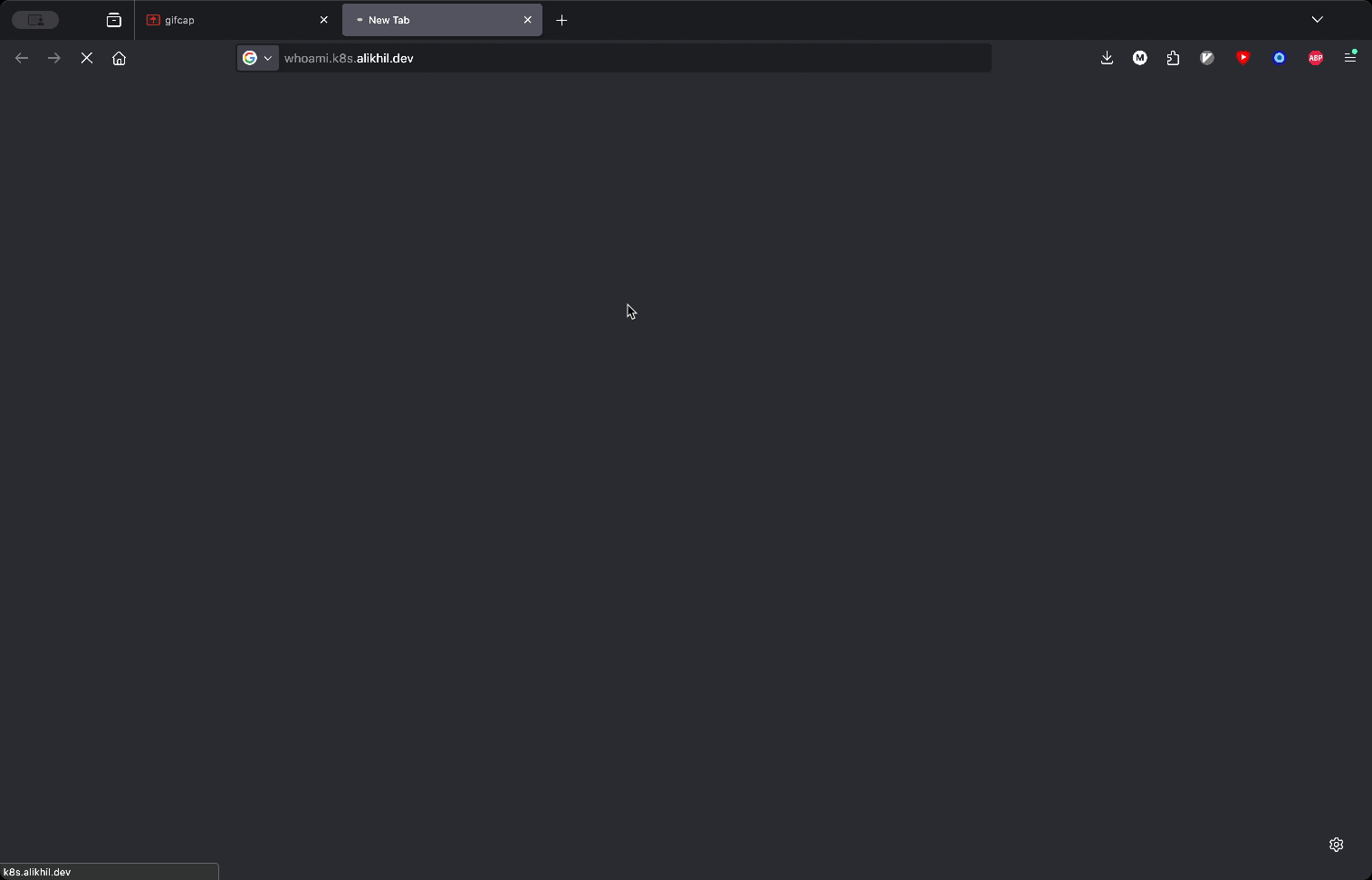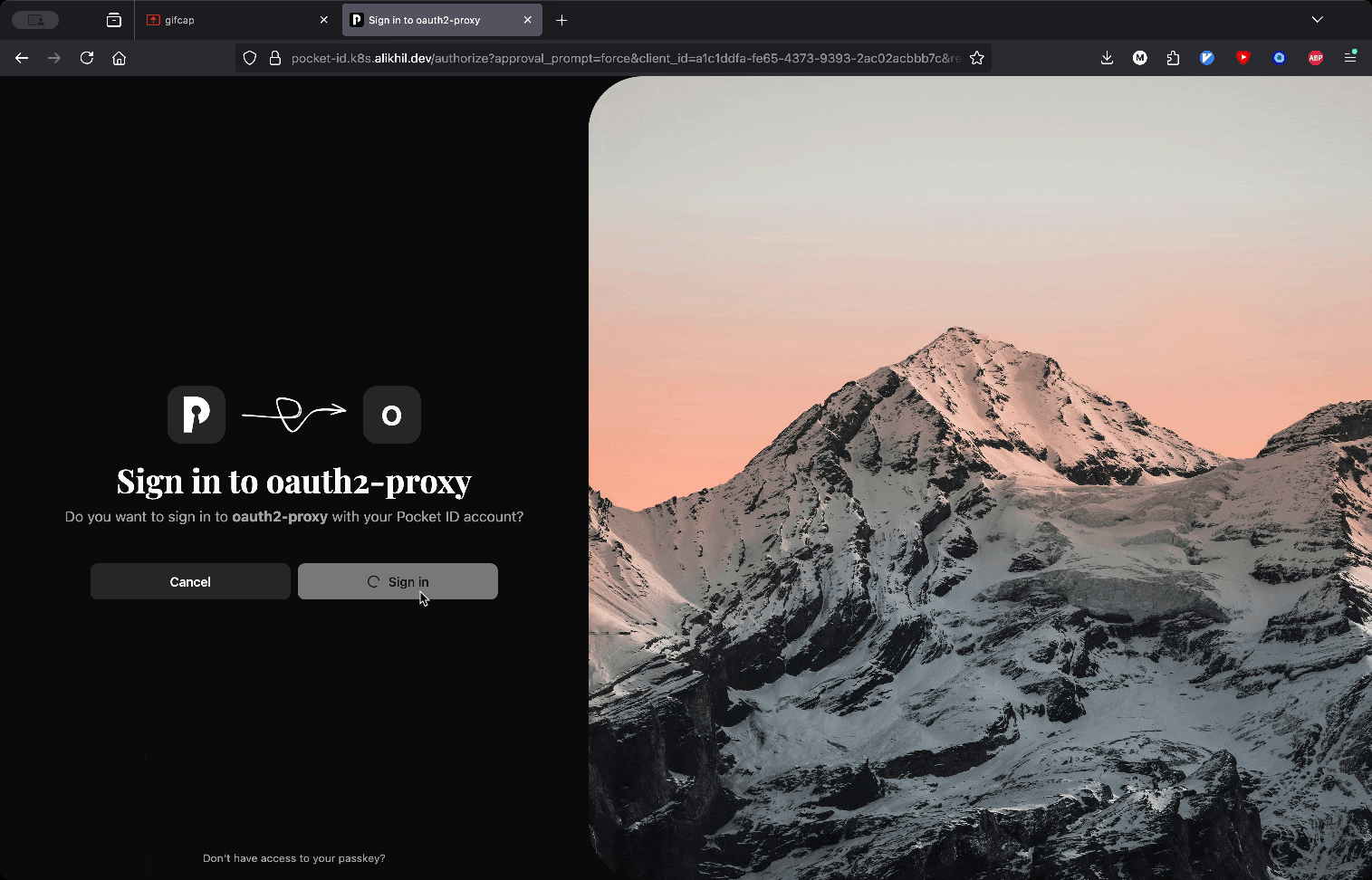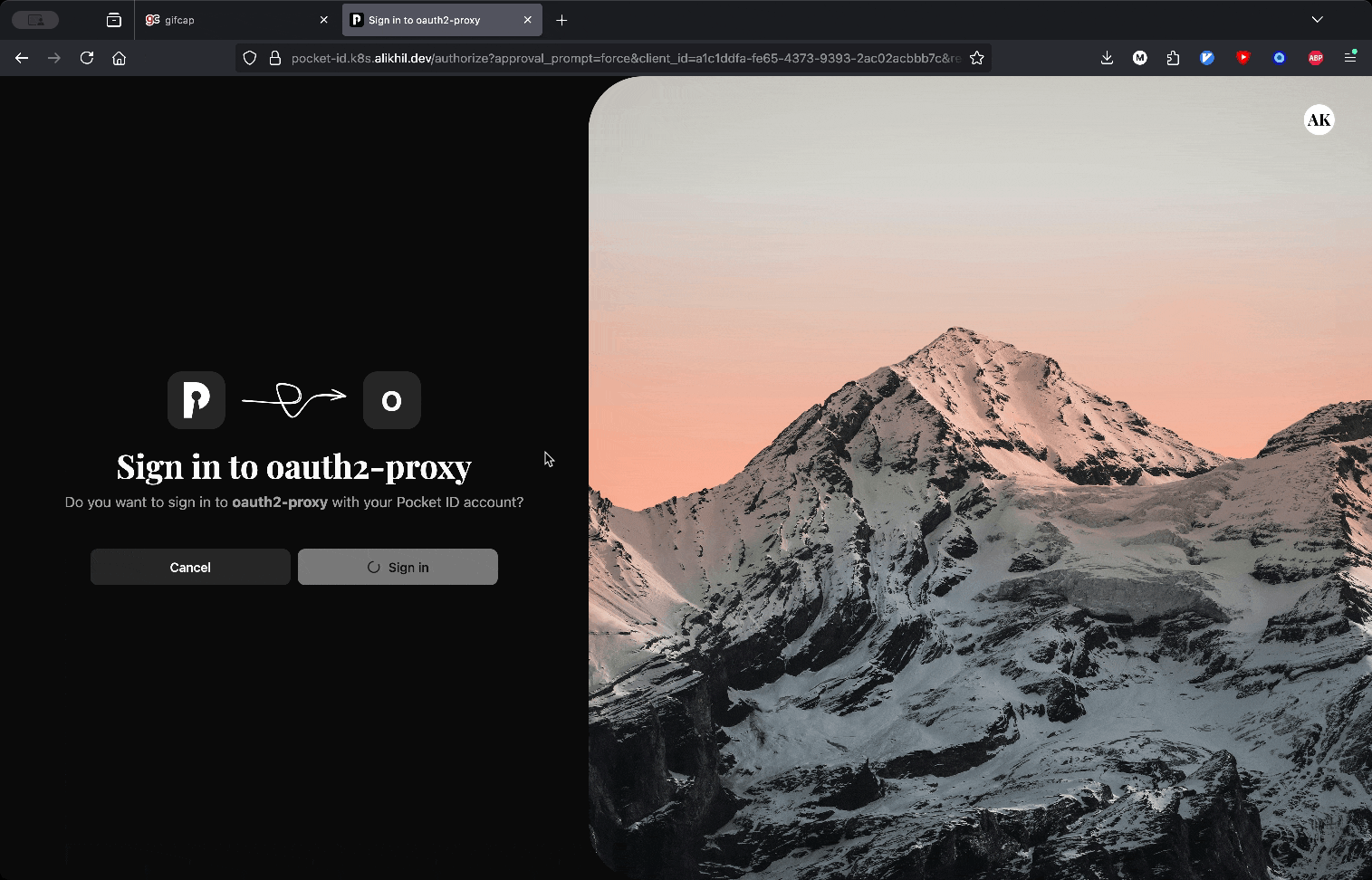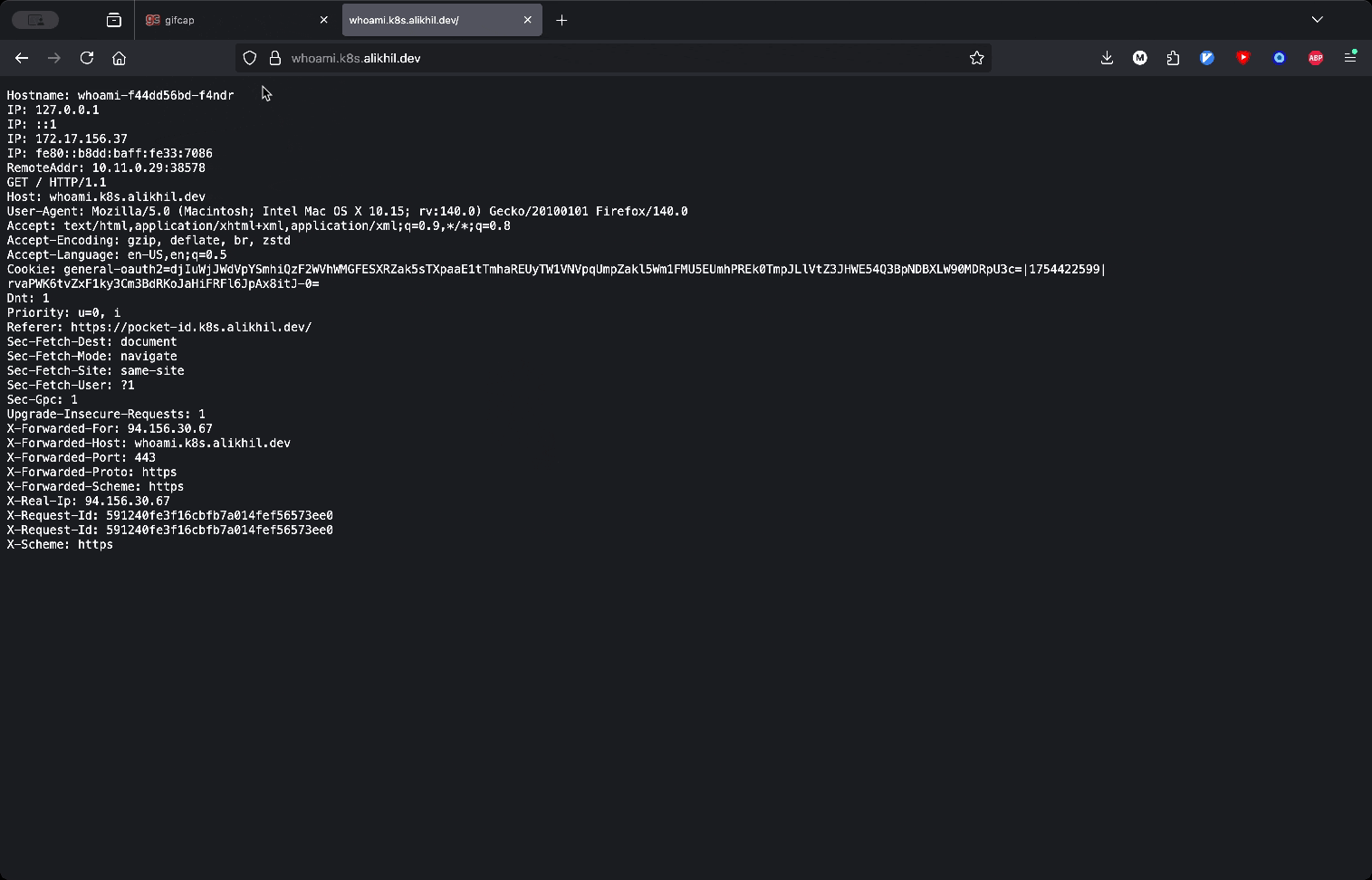
Go to whoami url and check if oauth2-proxy redirects you to Pocket ID like in the demo:
Takeaways
Later, when you need to protect any service in Kubernetes with oauth2-proxy, you simply need to add two annotations to your Ingress resource:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: "https://k8s.alikhil.dev/oauth2/start?rd=https://$host$request_uri$is_args$args"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: http://oauth2-proxy.oauth-example.svc.cluster.local:80/oauth2/auth